JOINT REPLACEMENT: KNEE REPLACEMENT
KNEE ARTHRITIS



ALL IMAGES Courtesy of Zimmer Biomet and Smith&Nephew
The knee joint is often depicted as a simple hinge joint, but upon closer inspection it is a very complex joint with a rotational-gliding mechanism and many important ligaments. TREATMENT SHOULD ACCORDINGLY BE CARRIED OUT BY A KNEE SPECIALIST.
Due to the high levels of stress to which the knee joints are exposed, wear and tear often occurs over the course of a person's life, leading to significant discomfort and a reduction in quality of life. Early sports injuries, misalignments or excess weight significantly promote this development.
In contrast to the hip joint, a so-called ball joint, in which the entire joint is always affected, only individual compartments (e.g. on the inside or behind the kneecap) can be treated in the knee joint.
AS PART OF THE TREATMENT OF KNEE JOINT OSTEOARTHRITIS (Knee Osteoarthritis), SURGICAL INTERVENTIONS MAY ALSO BE NECESSARY IN ADDITION TO CONSERVATIVE MEASURES:
- JOINT-PRESERVING OPERATIONS ON THE KNEE JOINT (CORRECTION OF MALPOSITIONS AND ANATOMICAL VARIATIONS MOSTLY BY MEANS OF MINIMALLY INVASIVE ARTHROSCOPY, SOMETIMES ALSO BY MEANS OF JOINT OPENING (MINI-OPEN). ENDOPROSTHETIC OPERATIONS ON THE KNEE JOINT (REPLACEMENT OF THE DESTROYED JOINT PARTS WITH ARTIFICIAL IMPLANTS MADE OF METAL AND HIGHLY CROSS-LINKED PLASTIC).
Artificial knee joints are divided into full and partial prostheses. I will carefully check which prosthesis is suitable for you based on a clinical examination and on X-rays or MRI scans.
Artificial joint replacement is a very successful and reliable treatment option in the advanced stages of osteoarthritis.
- Cemented or cement-free partial joint replacement using sled prostheses (internal or external) Cemented partial joint replacement using PFJ or Wave prosthesis (patellar surface replacement) Cemented complete surface replacement (classic: the "knee prosthesis") EXTRA stabilizing implants or axis-guided prostheses INLAYS as meniscus replacement made of highly cross-linked polyethylene

During the operation, the knee joint is accessed from the front and the knee is bent and stretched several times during the operation. The outer and inner ligaments and sometimes also the cruciate ligaments are carefully protected during the operation.
To ensure that you experience as little pain as possible after the operation, pain medication is administered by injection during the operation (LIA = local infiltration anesthesia).
KNEE PROSTHESIS IN MAINZ AND WIESBADEN IN THE ENDOPROTHETICUM
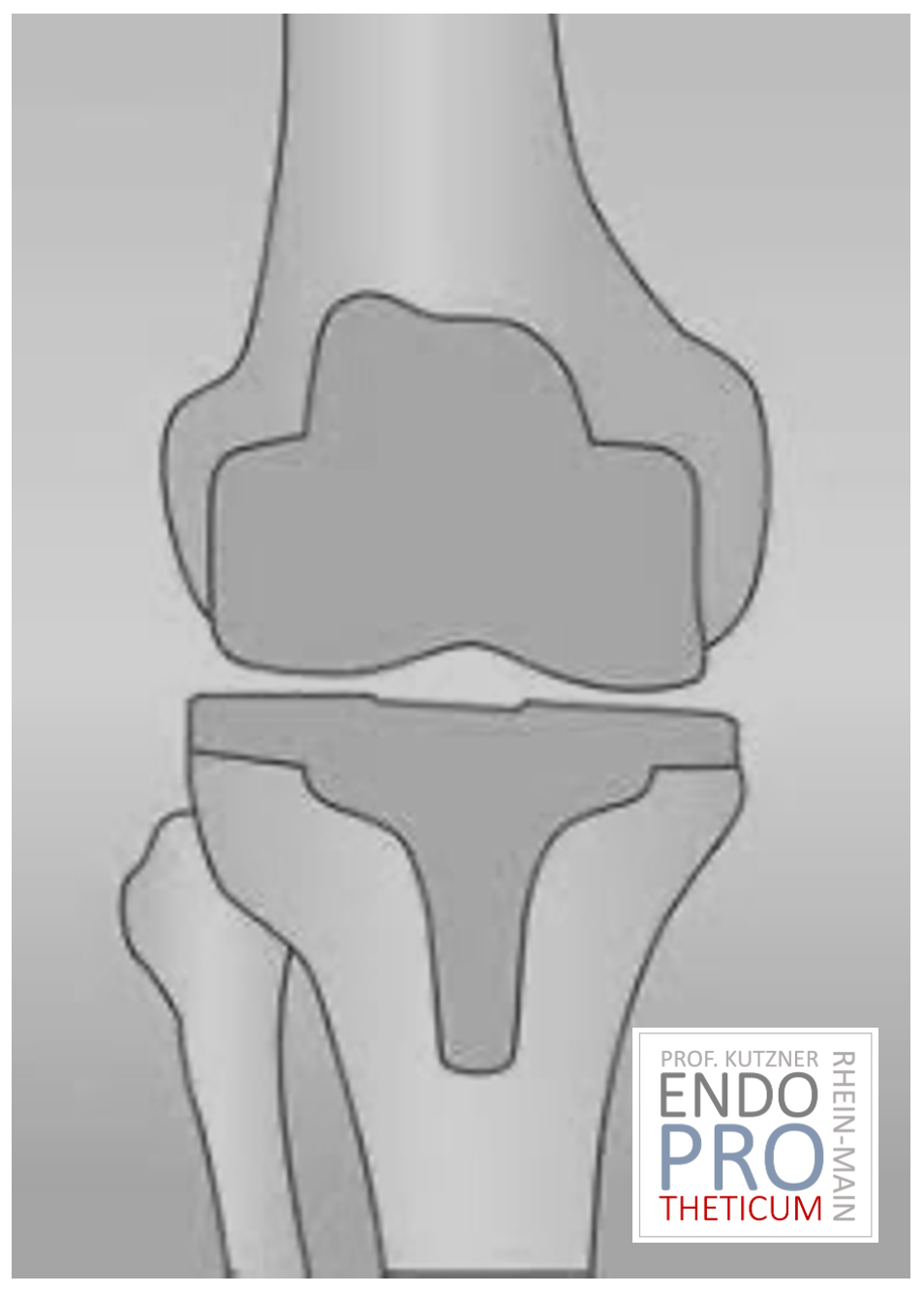
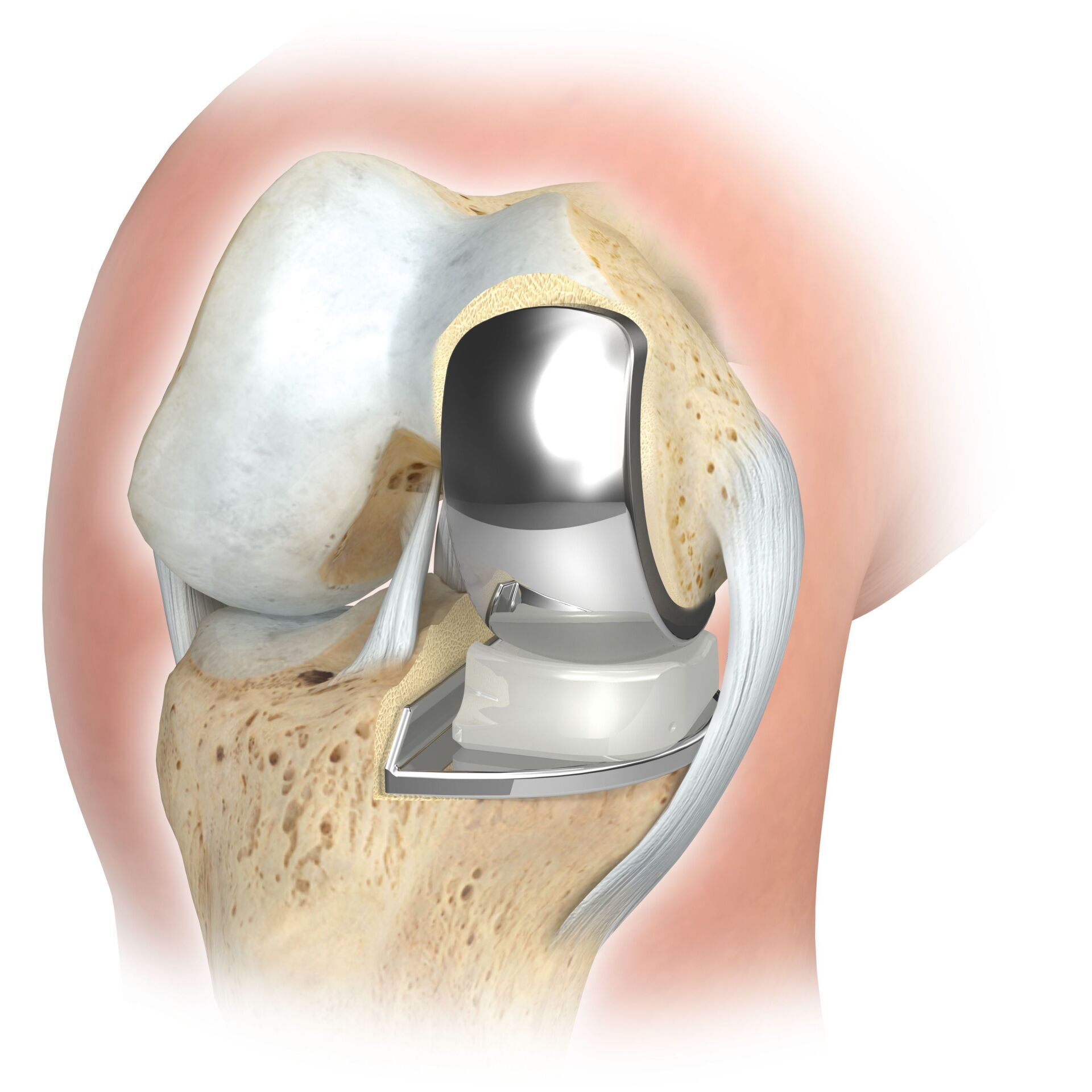
SLIDE PROSTHESIS
Partial knee replacement is possible in all areas of the joint, but is most commonly performed on the inside of the knee joint and is often referred to colloquially as a sled prosthesis. Similar to a full prosthesis, the defective cartilage is replaced with a new surface and a plastic inlay is inserted in between. For a partial prosthesis, all ligament structures, especially the cruciate ligaments, must be largely intact.

SURFACE REPLACEMENT
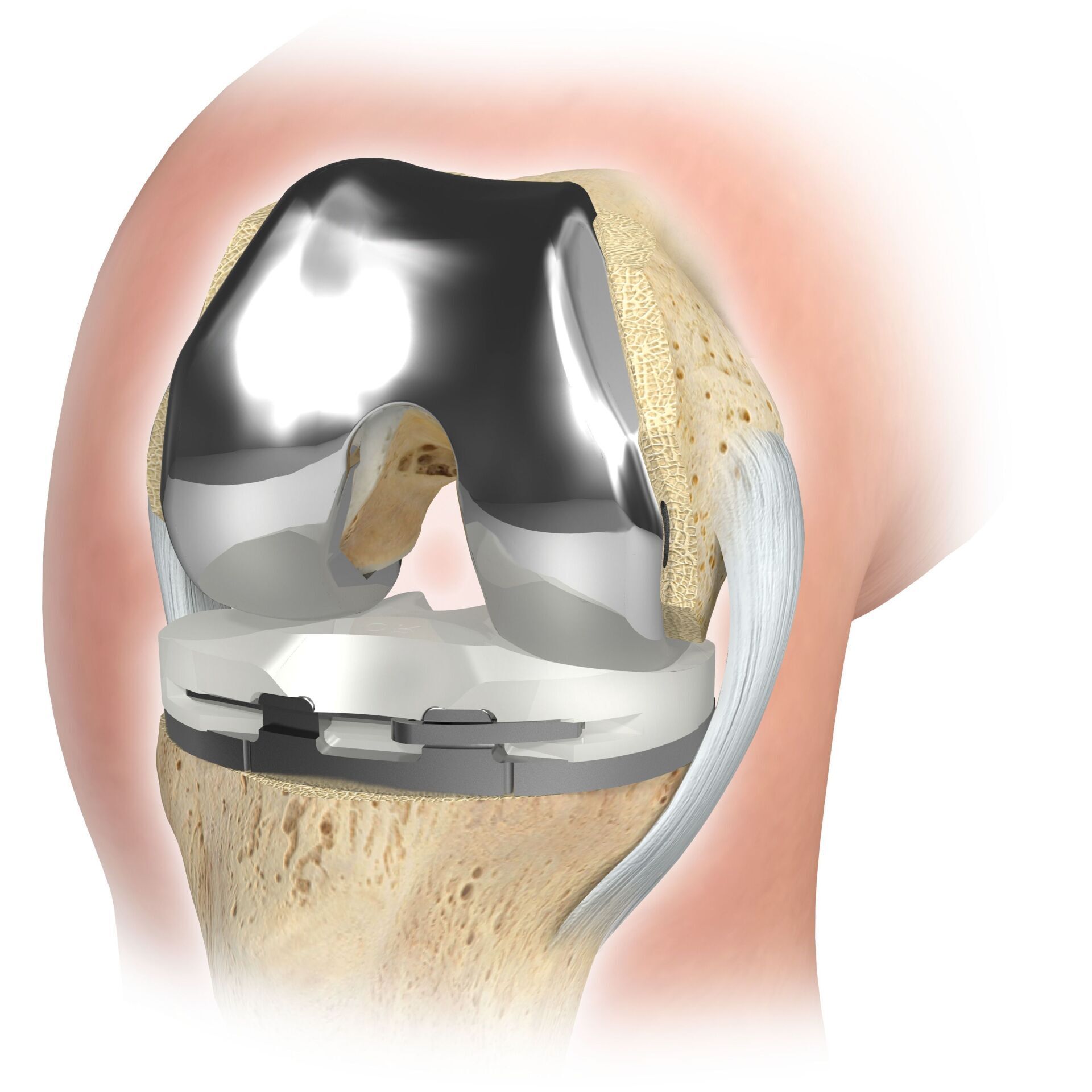
KNEE REPLACEMENT (ARTIFICIAL KNEE JOINT)

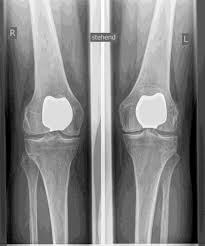
The artificial knee joint replaces the cartilage surface destroyed by arthrosis. The underlying bone on the thigh and tibial head remains intact. Some people compare a modern artificial knee joint to a crown on a tooth; the exact term is the so-called bicondylar surface replacement. Between the new surfaces on the thigh and lower leg is the so-called inlay made of a specially hardened white plastic, which can be seen in the X-ray image as the gap between the metal parts.
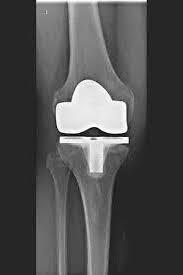
SMALL IMPLANTS / REPLACEMENT OF THE KNEECAP JOINT

The kneecap (patella) runs as an isolated bone in a groove of the thigh bone and, as the femoropatellar joint, represents one of three compartments of the knee joint.
It is fixed with tendons and ligaments and enables active extension of the knee joint.
Disturbances in mobility or instability as well as the shape of the kneecap (dysplasia) can lead to cartilage damage and arthrosis ISOLATED IN THE patellofemoral joint. IF THE OTHER COMPARTMENTS ARE FREE OF ARTHRITIS, an isolated partial joint replacement of the kneecap-posterior surface joint is possible.



PROF. KUTZNER: YOUR KNEE SPECIALIST IN MAINZ AND WIESBADEN
AS A KNEE SPECIALIST, I WOULD BE HAPPY TO PROVIDE YOU WITH IN-DEPTH ADVICE ON THE DIFFERENT THERAPY OPTIONS!