Advancements in Short-Stem Total Hip Arthroplasty: A Comprehensive Guide
Advancements in short-stem total hip arthroplasty
Total hip arthroplasty (THA), commonly known as hip replacement surgery, has seen significant advancements over the years. One of the most notable innovations is the development of short-stem implants. These implants offer numerous benefits over traditional long-stem prosthetics, including improved bone preservation, faster recovery times, and better outcomes for patients. This comprehensive guide will explore the advancements in short-stem total hip arthroplasty, detailing the technology behind these implants, the surgical techniques involved, and the advantages they offer.
The Evolution of Hip Replacement Implants
Traditional Long-Stem Implants
For decades, traditional long-stem implants were the standard for hip replacement surgeries. These implants require the removal of a significant portion of the femoral bone to accommodate the long stem. While effective, they posed several challenges, including:
- Extensive Bone Removal: A large portion of the femur must be removed to fit the implant.
- Higher Risk of Thigh Pain: The long stem can cause pain and discomfort in the thigh.
- Complex Revision Surgeries: If a revision surgery is needed, the extensive bone removal complicates the procedure.
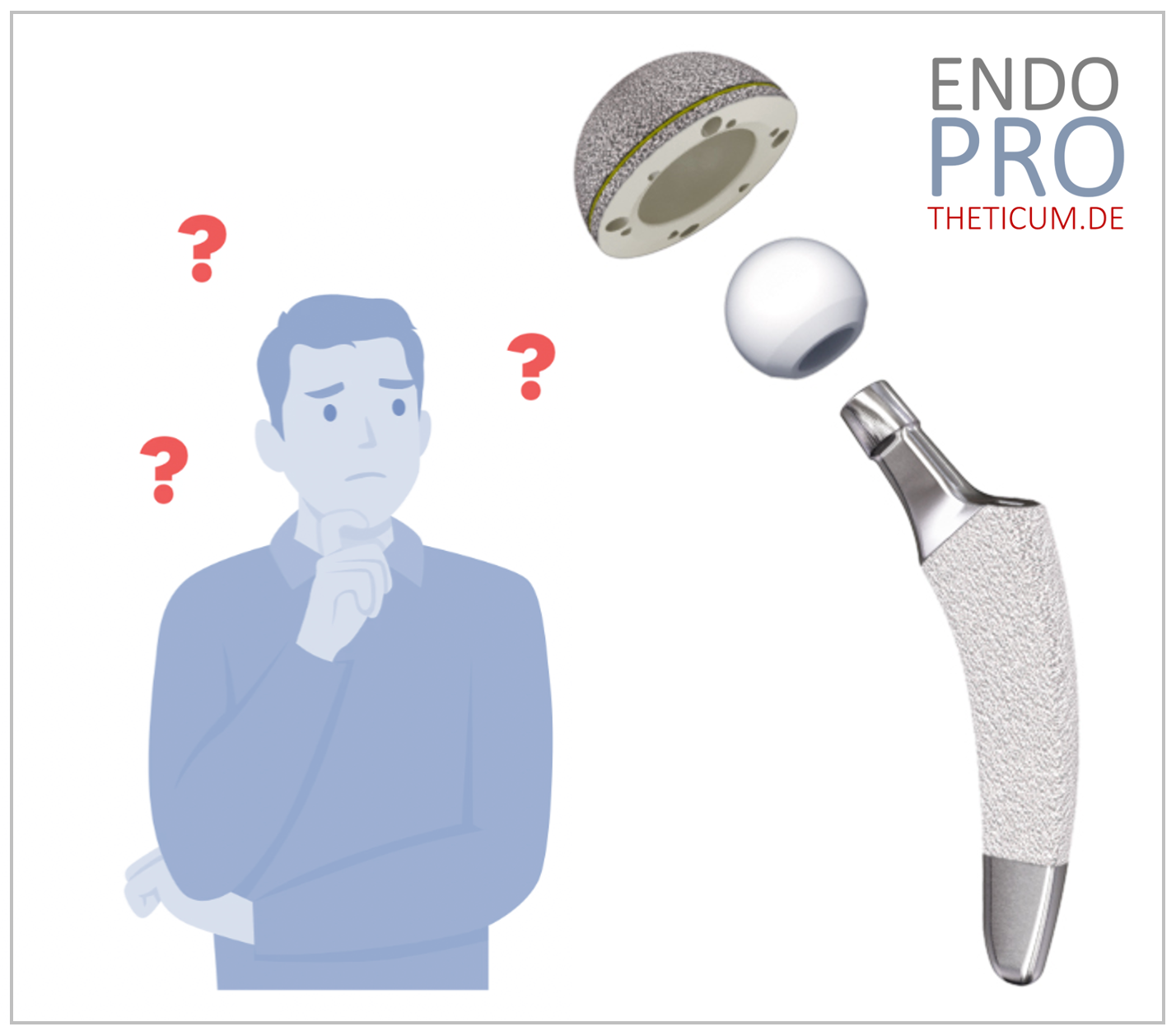
The Rise of Short-Stem Implants
Short-stem implants were developed to address these challenges. By requiring less bone removal, they preserve more of the patient’s natural bone, reduce the risk of thigh pain, and simplify future revision surgeries. The design of short-stem implants allows for a more anatomical fit, which promotes better load distribution and stability.
Technological Advancements in Short-Stem Implants
Material Innovations
The materials used in short-stem implants have seen significant improvements. Modern implants are made from advanced biocompatible materials such as titanium alloys and highly cross-linked polyethylene. These materials offer several benefits:
- Durability: Enhanced wear resistance and longevity.
- Biocompatibility: Reduced risk of adverse reactions.
- Improved Load Distribution: Better mimicry of natural bone properties.
Design Enhancements
The design of short-stem implants has also evolved, focusing on:
- Anatomical Fit: Better alignment with the patient’s natural bone structure.
- Optimized Load Distribution: Even distribution of mechanical stress across the femur.
- Stability: Enhanced initial and long-term stability.
Surgical Techniques for Short-Stem Total Hip Arthroplasty
Preoperative Planning
Preoperative planning is crucial for the success of short-stem total hip arthroplasty. This involves:
- Patient Evaluation: Assessing the patient’s overall health, bone quality, and specific needs.
- Imaging: Using advanced imaging techniques such as X-rays, CT scans, and MRI to plan the surgery.
- Custom Implant Selection: Choosing the appropriate implant size and design based on the patient’s anatomy.
Minimally Invasive Surgical Techniques
Short-stem implants are often placed using minimally invasive surgical techniques, which offer several benefits:
- Smaller Incisions: Reduced tissue damage and faster healing.
- Less Blood Loss: Lower risk of complications during surgery.
- Quicker Recovery: Patients can start rehabilitation sooner.
The Surgical Procedure
- Anesthesia: General or regional anesthesia is administered to ensure the patient is pain-free.
- Incision: A small incision is made over the hip joint.
- Joint Access: The hip joint is dislocated to expose the damaged femoral head.
- Bone Preparation: The damaged femoral head is removed, and the femur is prepared to receive the short-stem implant.
- Implant Insertion: The short-stem implant is carefully inserted into the femur.
- Reconstruction: The hip joint is reassembled, ensuring proper alignment and stability.
- Closure: The incision is closed, and a sterile dressing is applied.
Benefits of Short-Stem Total Hip Arthroplasty
Bone Preservation
One of the primary benefits of short-stem implants is the preservation of bone stock. By requiring less bone removal, these implants maintain the structural integrity of the femur, which is crucial for future revision surgeries and overall joint health.
Enhanced Recovery
Patients who undergo short-stem total hip arthroplasty often experience faster recovery times. The minimally invasive nature of the surgery, combined with reduced tissue damage, allows for quicker rehabilitation and a faster return to daily activities.
Reduced Risk of Thigh Pain
The anatomical design of short-stem implants reduces the risk of thigh pain, a common issue with traditional long-stem implants. The shorter stem minimizes pressure on the femoral cortex, leading to greater patient comfort and satisfaction.
Better Outcomes for Younger Patients
Short-stem implants are particularly beneficial for younger, more active patients. These patients are likely to require revision surgery in the future, and the bone-preserving nature of short-stem implants makes revisions easier and more successful. Additionally, the enhanced stability and quicker recovery times allow younger patients to maintain their active lifestyles.
Long-Term Outcomes and Patient Satisfaction
Longevity of Implants
Advancements in materials and design have significantly improved the longevity of short-stem implants. Studies have shown that these implants can last 15 to 20 years or more, depending on factors such as patient activity level and overall health.
Patient Satisfaction
Patient satisfaction rates for short-stem total hip arthroplasty are high, with many patients reporting significant improvements in pain, mobility, and overall quality of life. The reduced risk of complications and quicker recovery times contribute to these positive outcomes.
Challenges and Considerations
While short-stem total hip arthroplasty offers many benefits, there are some challenges and considerations to keep in mind:
- Patient Selection: Not all patients are suitable candidates for short-stem implants. Factors such as bone quality, anatomy, and activity level must be considered.
- Surgeon Experience: The success of the procedure depends on the surgeon’s experience and skill with short-stem implants.
- Potential Complications: As with any surgical procedure, there are risks, including infection, dislocation, and implant failure.
Future Directions in Short-Stem Total Hip Arthroplasty
Ongoing Research
Research continues to refine and improve short-stem implants. Areas of focus include:
- Material Innovations: Developing new materials that enhance durability and biocompatibility.
- Design Improvements: Creating implants that better mimic the natural anatomy and load distribution of the hip joint.
- Surgical Techniques: Advancing minimally invasive techniques to further reduce recovery times and improve outcomes.
Personalized Medicine
The future of short-stem total hip arthroplasty may also involve more personalized approaches. This includes:
- Custom Implants: Using 3D printing and other technologies to create custom implants tailored to the patient’s specific anatomy.
- Precision Surgery: Utilizing advanced imaging and robotic-assisted techniques to ensure the highest level of precision during surgery.
Conclusion
Short-stem total hip arthroplasty represents a significant advancement in the field of hip replacement surgery. With benefits such as improved bone preservation, faster recovery, reduced risk of thigh pain, and better outcomes for younger patients, short-stem implants offer a promising alternative to traditional long-stem prosthetics. Ongoing research and technological advancements continue to enhance the efficacy and safety of these implants, providing patients with better options for hip joint replacement.
As with any medical procedure, it is essential for patients to discuss their options with a qualified healthcare provider to determine the best course of action based on their individual needs and circumstances. With the right approach, short-stem total hip arthroplasty can lead to significant improvements in pain relief, mobility, and overall quality of life.
TERMIN VEREINBAREN?
Gerne können Sie einen Termin sowohl telefonisch, als auch online vereinbaren.